13

Eastman Tritan™ copolyester is raising the bar for durability and cleanability in medical devices and housings. BPA-free Tritan’s attributes include exceptional clarity, toughness, improved heat and chemical resistance, and more. It’s also easy to process due to its unique chemical makeup relative to traditional thermoplastics. This blend of processing and performance properties provides greater advantages compared with other commonly used polymers. Available in clear and opaque formulations, Tritan offers many benefits to enhance innovative device designs:
Clear formulations of Tritan
- Greater toughness, heat resistance, processability, and design freedom
- Clarity, color stability, and functional integrity after sterilization
- Outstanding chemical resistance to lipids, IPA, disinfecting agents, and bonding solvents and adhesives
Opaque formulations of Tritan
- Excellent functionality and reliability for device housings
- Compatibility with aggressive disinfection and the daily impact stresses that come with greater portability
- Color and functionality following sterilization with gamma and e-beam irradiation
- Reliable color matching
- Flame-retardant properties (Tritan MXF121 copolyester)
- Fire retardant—UL 94 V-2 rating @ 1.5 mm
- Excellent resistance to chemicals and lipids
- Meets hospital Environmentally Preferable Purchasing (EPP) guidelines—made without halogens or ortho-phthalate plasticizers
- Clear and opaque formulations—color matching available
- Excellent durability—high impact strength and toughness
- Fast cycle times
Check out the Tritan Medical Toolkit to learn more about the advantages of Tritan for different molded parts.
15

We’re excited to share our industry-leading products and technical expertise at Medical Design & Manufacturing (MD&M) West next month in Anaheim, California. We hope to see you there!
Tuesday, February 5, 11:45 a.m.–1:00 p.m., 212AB
Uncovering medical device failure modes and infection transmission pathways to inform better material testing methods, selection, and design: A panel discussion
Wednesday, February 6, 11:45 a.m.–1:00 p.m., 212AB
Meet one on one with members of our medical device and packaging teams at these sessions:
Thermoplastic Elastomer Powder and Its Benefits in Printing Medical Devices
Thursday, February 7, 9:15–10:00 a.m., 208B, Carolin Vogel
Choosing the Right Polymers for Superior Manufacturing and Durability: What Hospitals Measure
Thursday, February 7, 10:15–11:00 a.m., Ellen Turner, Thomas Meehan

10

Eastman will be exhibiting at Medical Design & Manufacturing (MD&M) West, Feb. 7–9, in Anaheim, California. Join us!
Visit our booth to speak one on one with an Eastman representative. Members of our medical devices team, including Ellen Turner, global market development manager, and Thomas Meehan, specialty plastics technical support, will be on hand to discuss plastic testing, selection, and design. Or attend one of our Lunch and Learn events to learn more about advancements in rigid medical packaging and medical devices.
Check out the conference schedule to start planning your time at MDMW 2019 today. We hope to see you there!

13

The material you choose for your medical devices can have a big impact on your brand’s image. In today’s healthcare environment, not all plastics can withstand exposure to the aggressive disinfectants being used in hospitals. If your device is showing outward signs of suffering from exposure to effects of disinfection, including yellowing, cracking, crazing, or paint peeling, it’s time to reconsider material selection.
Educating product managers about the attributes of different plastics can help better shape brand positioning. For example, cracks and crazes can lead to pooling of aggressive disinfectants and leakage into the sensitive electronics that make the device function. Choosing a more chemically resistant polymer prevents this by strengthening device durability and reducing maintenance time. As a result, the working life of the device increases and maintenance and replacement costs go down.
With this information, the product manager can position the brand as being resistant to the physical handling or moving of devices despite more frequent cleaning and use of harsh disinfectants. They can present brand devices as having a longer service life, keeping their “new” look longer, and being more durable. This positioning can also be used by hospitals and clinics, which can improve their image by purchasing more durable equipment that looks better because it is better.
By choosing materials with better quality and performance, manufacturers can help product managers position the brand as having those qualities as well.
9
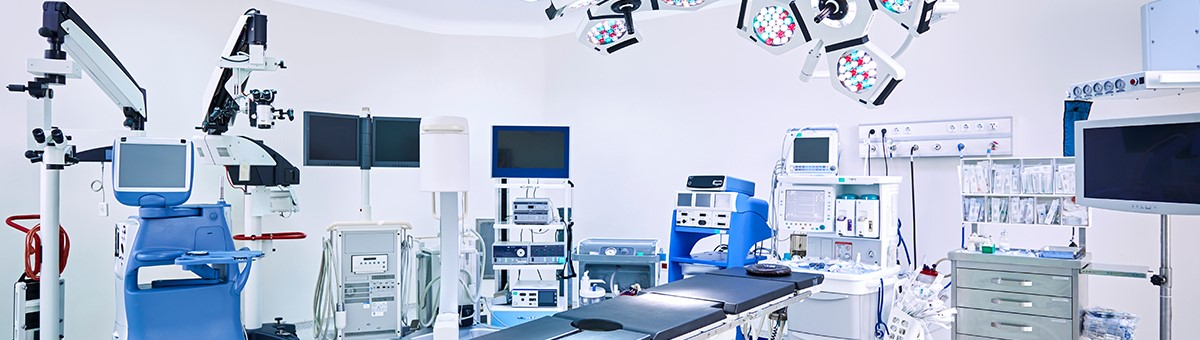
Medical device failures are a common—and costly—occurrence. They can lead to a product recall, affect the product development cycle, and result in extra expenses for manufacturers. The reasons devices fail can be complex, making it difficult for quality engineers to classify the problem.
What can quality engineers do to remedy this problem? Consider these factors:
- Understand why failures occur: Most device failures are caused by a misunderstanding of how a material’s properties, processing, and environment work together. In many cases, failures can result from a combination of wrong material selection, poor chemical resistance, high-stress design, or inconsistencies in manufacturing processes.
- Collaborate with your supplier: Working with material suppliers on material selection, testing, part and tooling design review, and secondary operations can give quality engineers access to knowledge and resources they may not otherwise have.
- Test your materials: Find a testing method that helps you choose the best plastic for your project. Eastman’s 4-step test for chemical resistance, for example, helps predict the reliability of a material after exposure to harsh cleaners and drugs commonly used in hospital settings.
Understanding the root causes of failures and working with industry experts to make better material choices can help quality engineers improve device design, have a more successful product launch, and save on costs.




 Close
Close





